Edge computing, with its ability to process data near its source, delivers secure and future proof solutions, without a round trip to the cloud. In this blog post, we explore examples of how data coming from a variety of simple sensors can be combined to produce better and new smart city services.
This blog is co-authored with guest author Glenn Meleder.
Smart City Challenges
The smart city market is in fast and constant evolution. This phenomenon is echoed in other markets, such an transport, energy, medical and retail.
The key drivers for implementing an edge computing solution include low latency, bandwidth limitation, privacy intrusion prevention and jittery networks. The upcoming 5G deployments won’t change this, since even 5G will not be able to deliver guaranteed low latency at scale, at the same time as dealing with high data throughput. And as sensory data is growing faster than networking capacity, the edge computing paradigm shift is the only sustainable option.
Looking forward, smart cities will have a lot on their to do list. Infrastructure-related services, will need to deliver:
- better security for citizens,
- more effective services,
- lowered maintenance costs,
- improved emergency services,
- better understanding of pollution (e.g. air, sound, light), leading to more effective counter measures,
- streamlined traffic
…and much more.
Status quo won’t work
The current trend of vertical or integrated solutions for each of the applications mentioned above is doomed to fail, due to complexity and operations costs. Think about it, if every solution requires its own sensor, communication pack, power supply, cloud management application, pricing, terms and conditions and operations procedure… ouch! A better solution is “data fusion” at the edge, and here’s how it works.
Data Fusion in action
Audio and video sensors provide the majority of raw sensory material needed in the smart city use cases listed above. And since the same sensor data is required for several applications, it follows that these should be reused across the different apps. This calls for an edge computing solution, where the video and audio streams are processed near the sensors, such that all applications can use and re-use the same high quality data.
Many smart city apps will greatly benefit from being able to process audio and video data together. By processing both data streams at the same time, application developers are able to deliver much improved and new services. Here are some good examples of where data fusion can be helpful:
- audio and video forensics can be provided to back a decision to send an alert to the emergency services following a detected accident
- degradation of infrastructures (e.g. graffiti or vandalism), as well as noisy or degraded vehicles can be detected using audio and identified using video
- the cause of a peak of particles pollution can be linked to categories of vehicle or malfunctioning machines.
Using a management platform, edge devices can be remote controlled and updated “over the air”. When combined with an app store (yes like Apple’s App Store or Google Play Store), the management platform provides smart city operators the ability to constantly update, add and upgrade their fleet of apps running at the edge. This also allows operation teams to react to cyber attacks in order to deploy counter measures and update apps quickly, thus reducing the impact of such attacks.
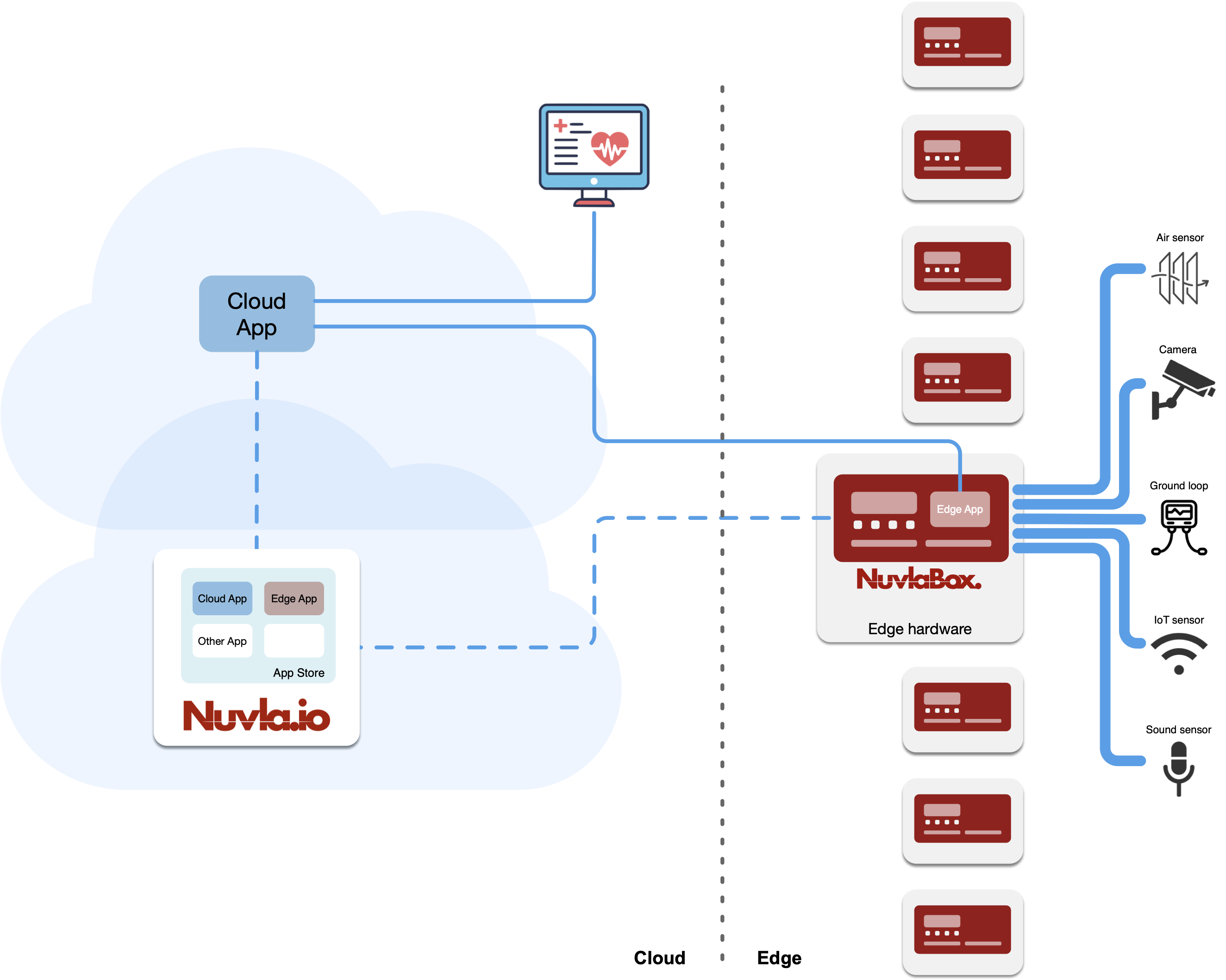
Nuvla edge architecture, with App Store and data fusion at the edge.
Data forensics as part of secure governance
Since the data is processed at the edge, no sensitive data is systematically streamed to the cloud for processing. Indeed, the data remains just for a short duration at the edge, from which only relevant events are derived, providing real-time actions or aggregated and anonymised trending data (e.g. traffic measurements, over time and by vehicle category). However, in some cases, we can “have our cake and eat it”. In the case where forensic data is required to support investigations, short video and audio sequences can be saved, compressed, encrypted, and finally, delivered to the appropriate authorities. Using asymmetric encryption, the edge system can encrypt the data with a public key, such that only the owners of the private key (e.g. law enforcement) can decrypt the data. As long as this process is part of proper governance procedures, the edge system will protect citizens, and deliver, in case of necessity and under strict control, forensic evidence to support investigations and follow-up actions.
Can we be future proof?
As we mentioned earlier, like many markets, smart cities are in constant evolution. This leads to the need of deploying solutions that are “future proof”. Edge computing software can ensure that future needs will be fulfilled without re-hauling the hardware infrastructure. This means that edge infrastructure can be deployed today and repurposed over time and the needs of the city evolves.
And this ability to evolve is not limited to smart cities, since it will equally apply to the other markets mentioned earlier.
Can we help?
We have experience with implementing edge solutions for smart cities and other markets, so don’t hesitate to contact us if you need support with assessing the potential benefits of edge computing.
As strong proponents of open source, open data and open systems, you can count on our independent advice.


